HVAC & R systems
Efficient HVAC & R systems ensure indoor comfort, air quality, and energy optimization. Below are the key types:
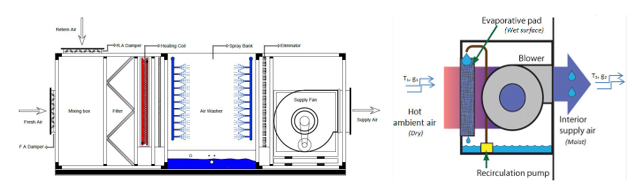
- Air Handling Unit (AHU) – AHUs regulate and circulate air by conditioning it with heating, cooling, filtering, and humidification before distributing it through ducts.
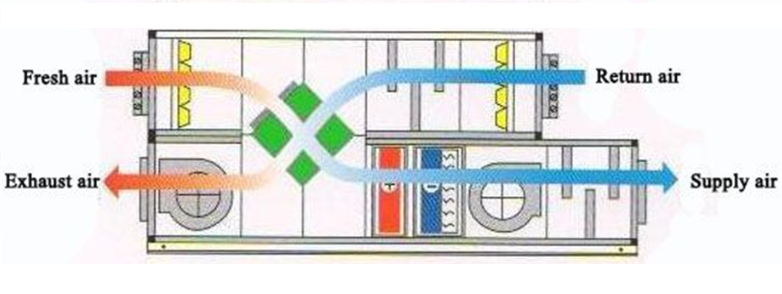
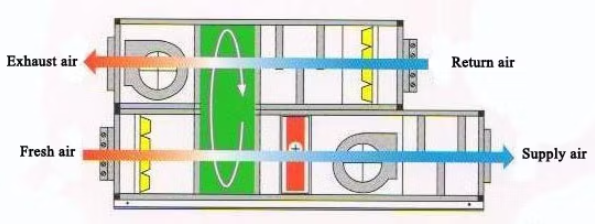
- Packaged System – A single-unit system for compact spaces, integrating heating and cooling.

- A Rooftop Unit (RTU) is a self-contained system installed on a building’s roof, designed for heating, cooling, and ventilation. It conditions air and distributes it through ductwork to the interior space. RTUs are commonly used in commercial and industrial buildings due to their space-saving design, ease of maintenance, and energy efficiency. On the contrary, AHU is a part of a larger system that requires external heating/cooling sources.

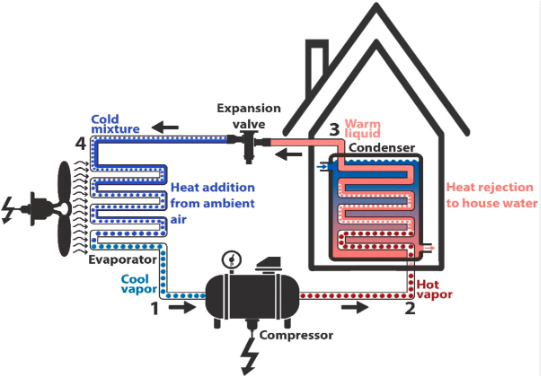
- Heat Pump – A heat pump is a device that transfers heat between indoor and outdoor environments using a refrigeration cycle. It provides both heating and cooling by reversing the refrigerant flow. In heating mode, it extracts heat from outdoor air, water, or the ground and delivers it indoors. In cooling mode, it removes indoor heat and releases it outside.
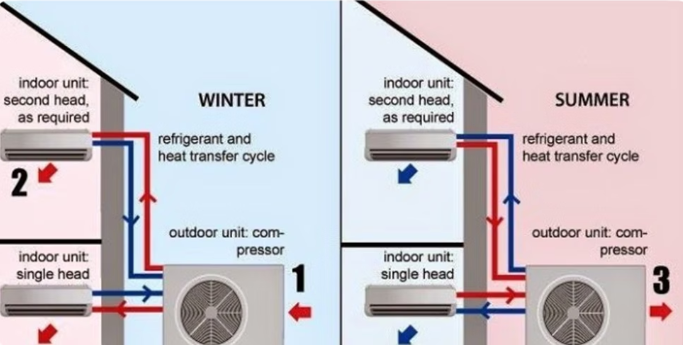
- Split System – Common in homes, with separate indoor and outdoor units for heating and cooling.
- A cooling tower is a heat rejection device that removes waste heat from a building or industrial process by evaporative cooling. It transfers heat from the circulating water to the air, lowering the water temperature before recirculating it to the chiller or condenser.
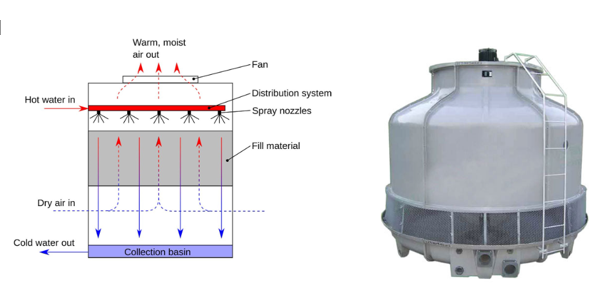
- An air washer or evaporative water cooler: Both cooling towers and air washers operate on the evaporative cooling principle, where heat is removed by water evaporation. However, their objectives differ: In a cooling tower, warm water from a system (e.g., a chiller or industrial process) is sprayed or distributed over a large surface, and air is passed through. Some of the water evaporates, absorbing heat and cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated for cooling equipment. Here, cooled water is the main goal. In an air washer, water is sprayed into an airstream, and as some of it evaporates, it reduces the air temperature while increasing humidity if needed. The cleaned, cooled air is then supplied to the conditioned space. Here, cooled air is the main goal. In both cases, the fundamental principle is heat removal through water evaporation, but the intended outcome differs—cooled water in cooling towers vs. cooled and conditioned air in air washers.
- Refrigeration Storage Warehouses – Industrial and commercial cold and frozen storage warehouses are temperature-controlled facilities designed to preserve perishable goods. They serve industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance. Cold Storage (0 to 10°C): Ideal for fresh produce, dairy, and beverages. Frozen Storage (-18°C and below): Preserves meat, seafood, and pharmaceuticals.


- District Heating & Cooling System – A centralized system distributing thermal energy to multiple buildings.
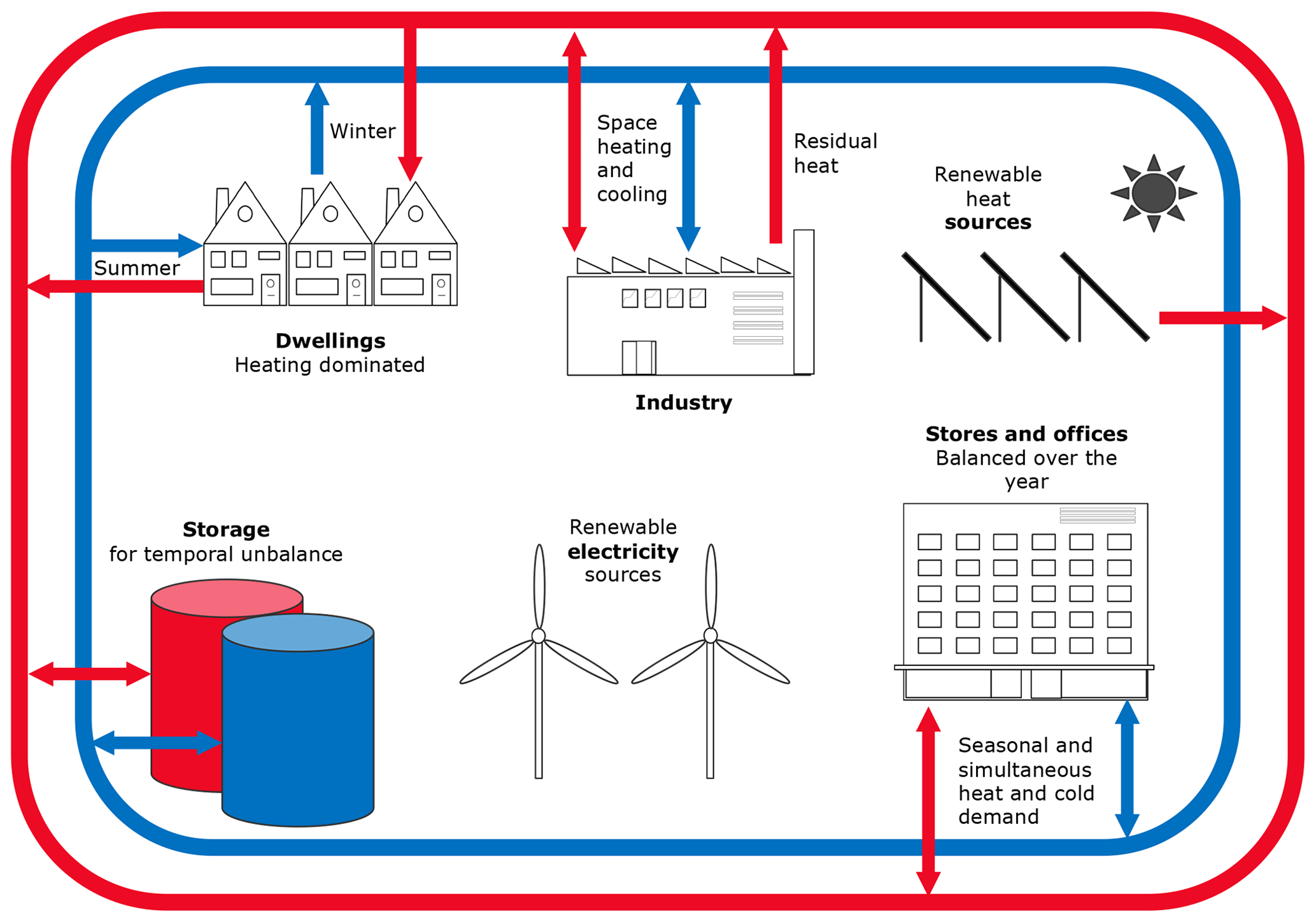
Each system is designed for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance, energy efficiency, and indoor air quality.
